I'm thrilled to share that our study is now published in Cell:
Extensive N4 cytosine methylation is essential for Marchantia sperm function.
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
This paper confirms our 4mC discovery in Marchantia sperm and takes it much further.
A thread: 0/13
Extensive N4 cytosine methylation is essential for Marchantia sperm function
Global N4 cytosine methylation in Marchantia polymorpha sperm regulates gene expression
and promotes sperm fertility.
[Not loaded yet]
Thanks Max!! 😁😁
[Not loaded yet]
A putative 4mC methyltransferase is found in rotifers (N4CMT) that's also thought to have arisen through horizontal gene transfer from bacteria which we talk about briefly in the paper. Wouldn't be surprised if there are others examples out there to be found!
[Not loaded yet]
Thanks Jake!! 😄
[Not loaded yet]
Thanks Sean!! 😁😁😁
[Not loaded yet]
Thanks Li! 😎
[Not loaded yet]
Thanks Tatsuya!! :)
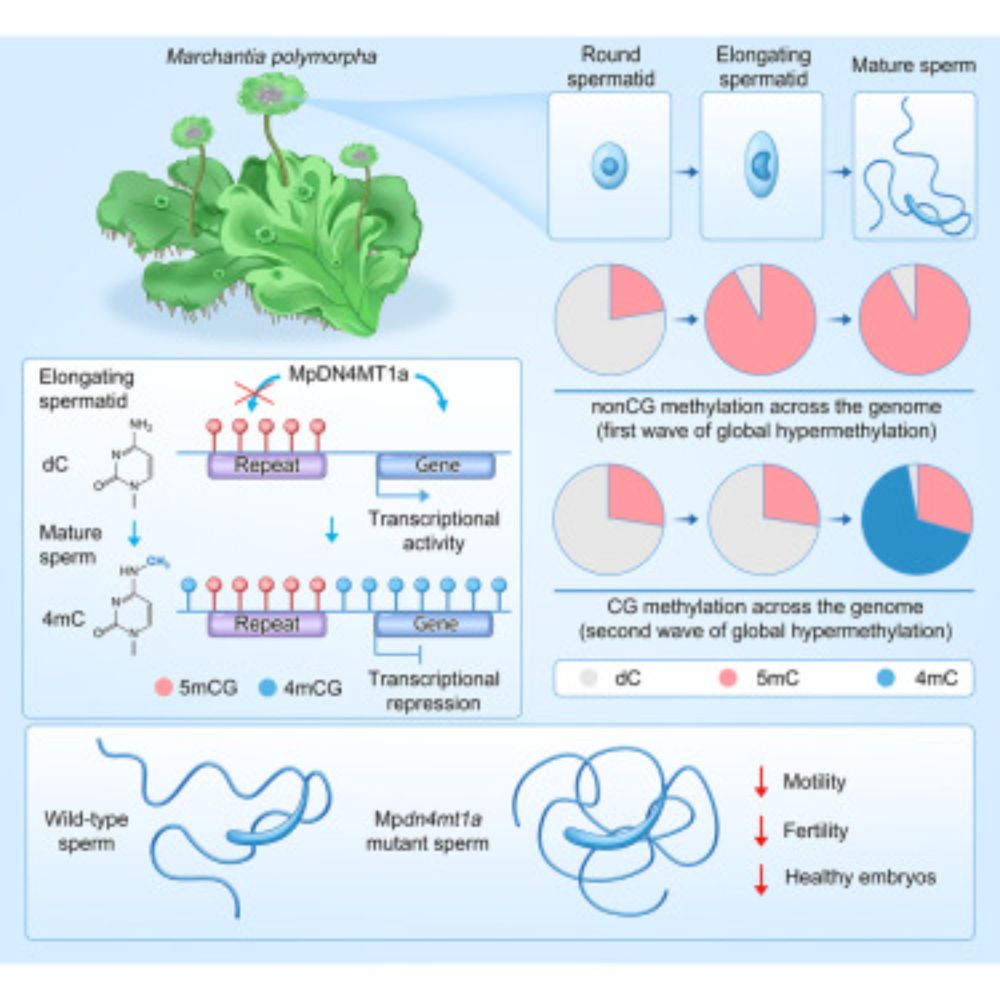
This work completes a story that started with strange bisulfite-seq anomalies during my PhD and ends with the discovery of a new epigenetic layer in eukaryotic reproduction.
Huge thanks to all co-authors, collaborators, and especially Xiaoqi Feng for guidance throughout.
13/13
We also propose that 4mC could act as a paternal imprint—for example, guiding PRC2 targeting after fertilization. This may explain why loss of paternal 4mC reduces embryo viability and disrupts development.
11/13
In summary, our study establishes:
4mC is a functional DNA modification in eukaryotes
MpDN4MT1a is a eukaryotic 4mC writer
5mC and 4mC mark distinct chromatin domains in sperm
4mC coordinates transcriptional shutdown, chromatin compaction, sperm motility, and fertility
12/13
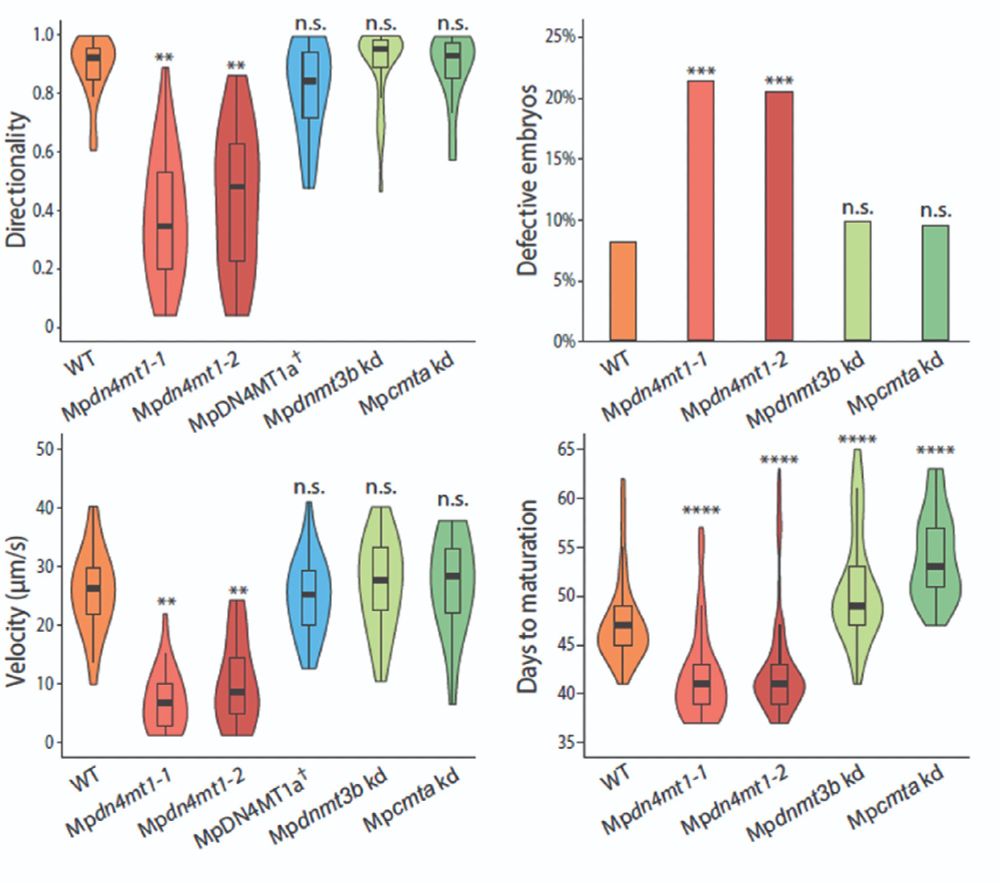
The motility defect is rescued by reintroducing wild-type MpDN4MT1a.
By contrast, sperm from global 5mC mutants show none of these distinctive phenotypes.
9/13
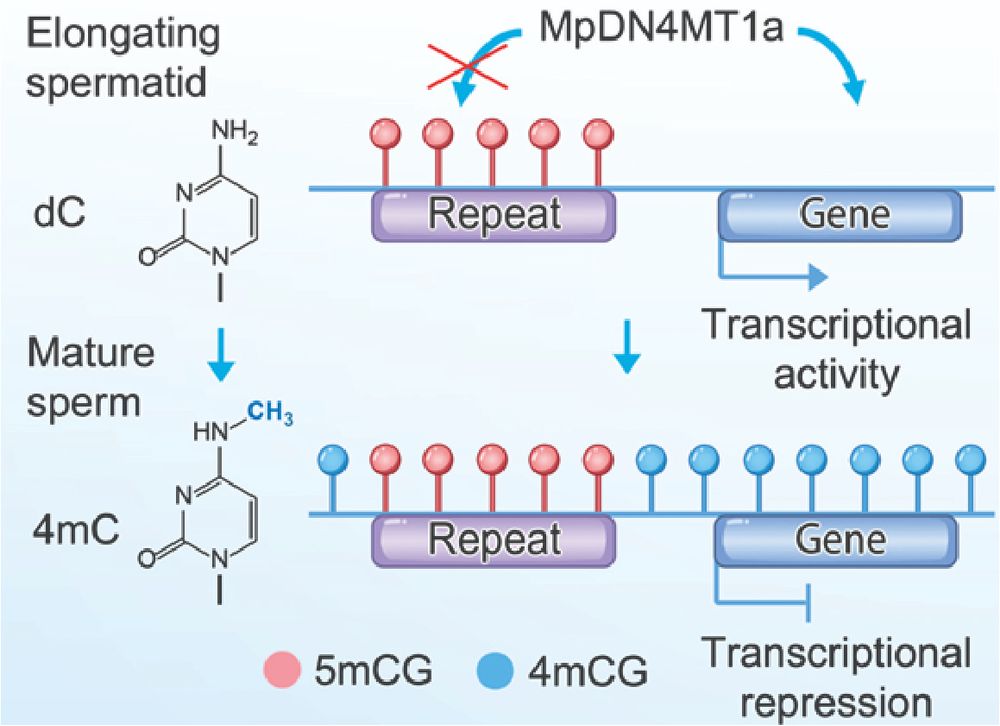
Why deposit 4mC in Marchantia sperm?
We see no evidence of dual-modified 4,5mC, suggesting that 5mC blocks 4mC. This creates a clear division: 4mC marks genes, 5mC marks repeats.
This allows global methylation for compaction while preserving the TE-specific 5mC signature.
10/13
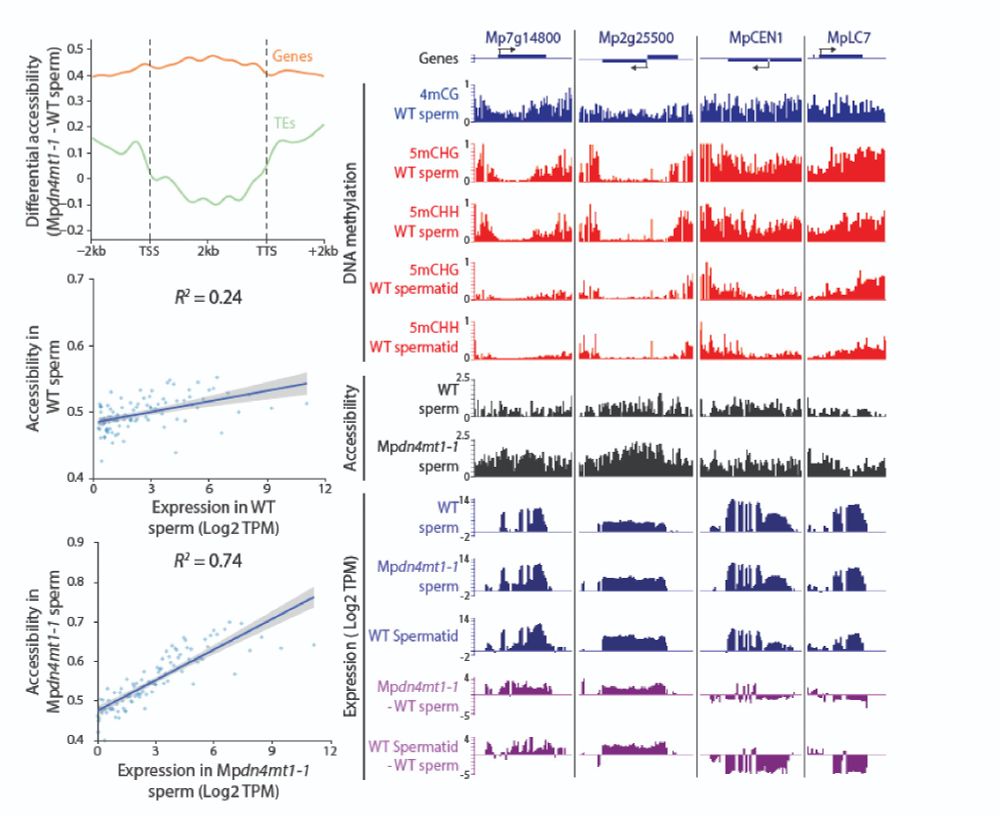
By contrast, transcripts for key sperm function genes—like CENTRIN1 and DYNEIN LIGHT CHAIN 7—are reduced, likely due to a dilution effect, helping explain the sperm motility defect in 4mC mutants.
7/13
We now know that 4mC is essential for multiple aspects of sperm function.
Sperm lacking 4mC are motility-defective, outcompeted by wild-type sperm, and produce developmentally compromised embryos.
8/13
We previously saw a correlation between 4mC loss and mis-regulated transcription in sperm, but now we uncover the mechanism:
4mC compacts chromatin, silences transcription, and completes the sperm epigenome transition.
5/13
ATAC-seq shows widespread open chromatin in mutants—especially where 5mC is absent at transcription start sites.
Careful RNA-seq analysis uncovered globally elevated expression. As a result, the mutant transcriptome resembles wild-type spermatids before 4mC is established!
6/13
We show that MpDN4MT1a, a eukaryotic homolog of bacterial 4mC methyltransferases, is the enzyme required for this modification.
Loss of MpDN4MT1a abolishes 4mC, and reintroduction of wild-type—but not the catalytic mutant—restores it.
3/13
The MpDN4MT1 gene appears to have originated via horizontal gene transfer from prokaryotes and has been retained for at least 200 million years— we detect it even in Lunularia cruciata, a liverwort from a distinct lineage to Marchantia.
4/13
In 2021, we described a novel wave of CG methylation in Marchantia polymorpha sperm and showed evidence that this mark was N4-methylcytosine (4mC) which is a very contentious modification in eukaryotes.
biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
1/13

Extensive N4 Cytosine Methylation is Essential for Marchantia Sperm Function
4-methylcytosine (4mC) is an important DNA modification in prokaryotes, but its relevance, and even presence in eukaryotes have been mysterious. Here we show that spermatogenesis in the liverwort Marc...
In our new paper, we use six methods to unambiguously validate the presence of extensive 4mC at CG sites across genic regions in mature sperm:
🧪 immunodot blot
🧪 LC-MS
🧬 Bisulfite-seq
🧬 SMRT-seq
🧬 4mC-TAB-seq
🧬 4mC-AMD-seq
2/13
[Not loaded yet]
Huge congratulations Tatsuya! Great start to the new year! 😁 🥳